A group of researchers of the Centre for Physical Chemistry and Nanocomposites of the Institute of Chemistry of the ASM (prof., dr.hab. Fliur Macaev, Dr. Veaceslav Boldescu, acad. Gheorghe Duca) has developed a new type of nanocapsules that can be more effective in tuberculosis treatment than the existing remedies.
At present, another group of researchers under supervision of Dr. Valeriu Crudu from the Laboratory of Microbiology and Morphology of Tuberculosis of the Institute of Phthisiopneumology "Chiril Draganiuc" deals with biological testing of the new anti-tuberculosis compounds.
The invention has been developed within the project "Nano-encapsulation of anti-TB drugs for targeted delivery" funded by USA, Canada, Sweden, Ukraine (STCU), and Moldova (ASM).
In comparison with the anti-tuberculosis agents that have been used in medicine, new nanocapsules can be easier delivered to the tuberculosis bacteria in the organism. It is a new technology that protects the thin tissue of the lung. At the site of action, nanocapsule discharges the active compound and make it available for the action against the bacteria. Simultaneously, free cyclodextrins act destructively against mycobacteria by caption of its structural parts (Fig. 1).
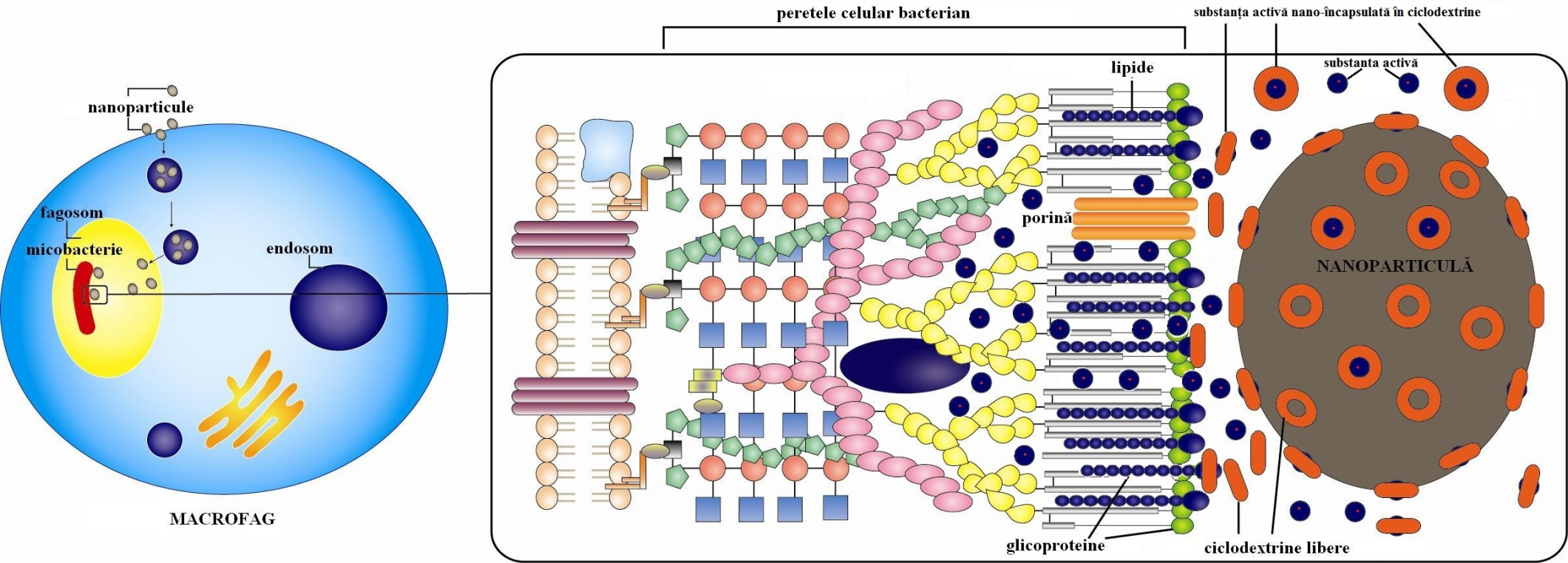
Fig. 1. Mechanism of action of nanocapsules formed of cyclodextrins and antituberculosis compounds
Results obtained in preclinical testing of compounds activity have shown that the nature of the cyclodextrin associated with biologically active compound influences its anti-tuberculosis activity. Thus, by combining various cyclodextrins with biologically active substances with a high antimycobacterial potential will be possible to obtain new anti-TB drugs with increased activity and reduced toxicity. |